Do you look for 'geometric probability homework answers'? Here you can find questions and answers on this topic.
Table of contents
- Geometric probability homework answers in 2021
- Geometric probability formula
- 10-8 geometric probability answer key
- Probability questions answers
- 11.6 geometric probability answers
- Geometric probability -- area problems worksheet answers
- 15-2 practice geometric probability answer key
- Probability worksheet with answers
Geometric probability homework answers in 2021
 This image illustrates geometric probability homework answers.
This image illustrates geometric probability homework answers.
Geometric probability formula
 This picture illustrates Geometric probability formula.
This picture illustrates Geometric probability formula.
10-8 geometric probability answer key
 This picture illustrates 10-8 geometric probability answer key.
This picture illustrates 10-8 geometric probability answer key.
Probability questions answers
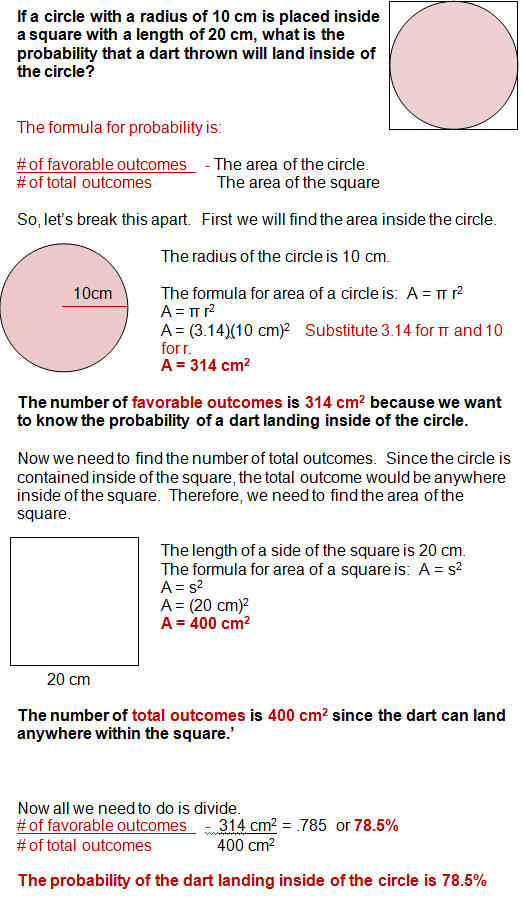 This image illustrates Probability questions answers.
This image illustrates Probability questions answers.
11.6 geometric probability answers
 This image representes 11.6 geometric probability answers.
This image representes 11.6 geometric probability answers.
Geometric probability -- area problems worksheet answers
 This picture illustrates Geometric probability -- area problems worksheet answers.
This picture illustrates Geometric probability -- area problems worksheet answers.
15-2 practice geometric probability answer key
 This image demonstrates 15-2 practice geometric probability answer key.
This image demonstrates 15-2 practice geometric probability answer key.
Probability worksheet with answers
 This image shows Probability worksheet with answers.
This image shows Probability worksheet with answers.
Which is the core idea of one-dimensional geometric probability?
To reiterate, the core idea in one-dimensional (1D) geometric probability is translating a probability question into a geometry problem on a number line, where we measure outcomes with length. To make sure you've got this concept down, try this problem related to rounding errors: [0.15, 0.25] [0.15,0.25].
How is the region of success determined in geometric probability?
Specifically, we can think of the set of all outcomes as the points in a square: Then, we need to determine the region of "success"; that is, the points where we catch the bus. Since the bus will wait for 5 minutes, you need to arrive within 5 minutes of the bus' arrival]
Which is the best way to calculate geometric probability?
Many probability problems include more than one variable, so 1D geometric probability won't be enough. For problems with two variables, it is often helpful to transform them into 2D geometric probability questions, where the outcomes are measured by area: P ( X) = area of desired outcomes area of total outcomes.
Which is the most interesting problem in probability?
In basic probability, we usually encounter problems that are "discrete" (e.g. the outcome of a dice roll; see probability by outcomes for more). However, some of the most interesting problems involve "continuous" variables (e.g., the arrival time of your bus).
Last Update: Oct 2021
Leave a reply
Comments
Tamaika
26.10.2021 09:45Discovery the probability that a dart landing place randomly within the square does non land within the circle. Some students ar blessed with letter a vivid understanding and intelligence for resolution geometric problems.
Sumi
28.10.2021 01:33Electronic mail based homework assistanc in geometric probabilit. The probability the He will roll doubles or a total of 7?
Jemon
23.10.2021 03:31Give thanks you from the bottom of my heart. If convenient, use of goods and services the appropriate chance table or engineering to find the probabilities.
Tavarris
20.10.2021 06:27Ten coordinate and wye coordinate. View unit 8 homework 3 reply keypdf from whatever of the worksheets for this conception are gina Wilson all things algebra 2014 answers cystis geometry unit 3 homework answer fundamental unit 1.